With the rapid advancement of technologies, introduction of innovation in almost every field, and developments in the world of healthcare, the Internet of Medical Things (ioMT or IoT) is seen as the most promising technology which will accelerate the way we diagnose, monitor, and treat diseases & patients. The opportunities within it are widespread and impactful, ranging from supply chain management to improving critical care and reducing healthcare expenses. While these opportunities have been widely studied, challenges have been somewhat ignored, although they are vital for the development of this technology and its implementation as a viable solution.
What is IoMT?
IOMT refers to the network of connected medical devices that involve the use of internet connectivity. This network could involve devices worn by patients, such as insulin pumps, or devices that are used by health care providers to monitor patient’s health remotely.
The role of IoMT in clinical care
With the rapid development of technology and the increasing demand of patients for quality medical care, the Internet of Medical Things (IOMT) is now playing an important role in clinical care. For example, a heart monitor can be used to monitor a patient’s condition and send data to doctors. This allows doctors to detect problems early and provide timely treatment. It also saves time because they don’t have to make multiple trips back and forth between patients’ homes or hospital rooms.
However, some people believe that IoMT may not be beneficial for all patients because it may cause privacy concerns or lead them into a false sense of security if they think their health problems are being monitored by someone else. As with any other technology, there will always be pros and cons but when used correctly this type could help improve many aspects of how we live our lives every day!
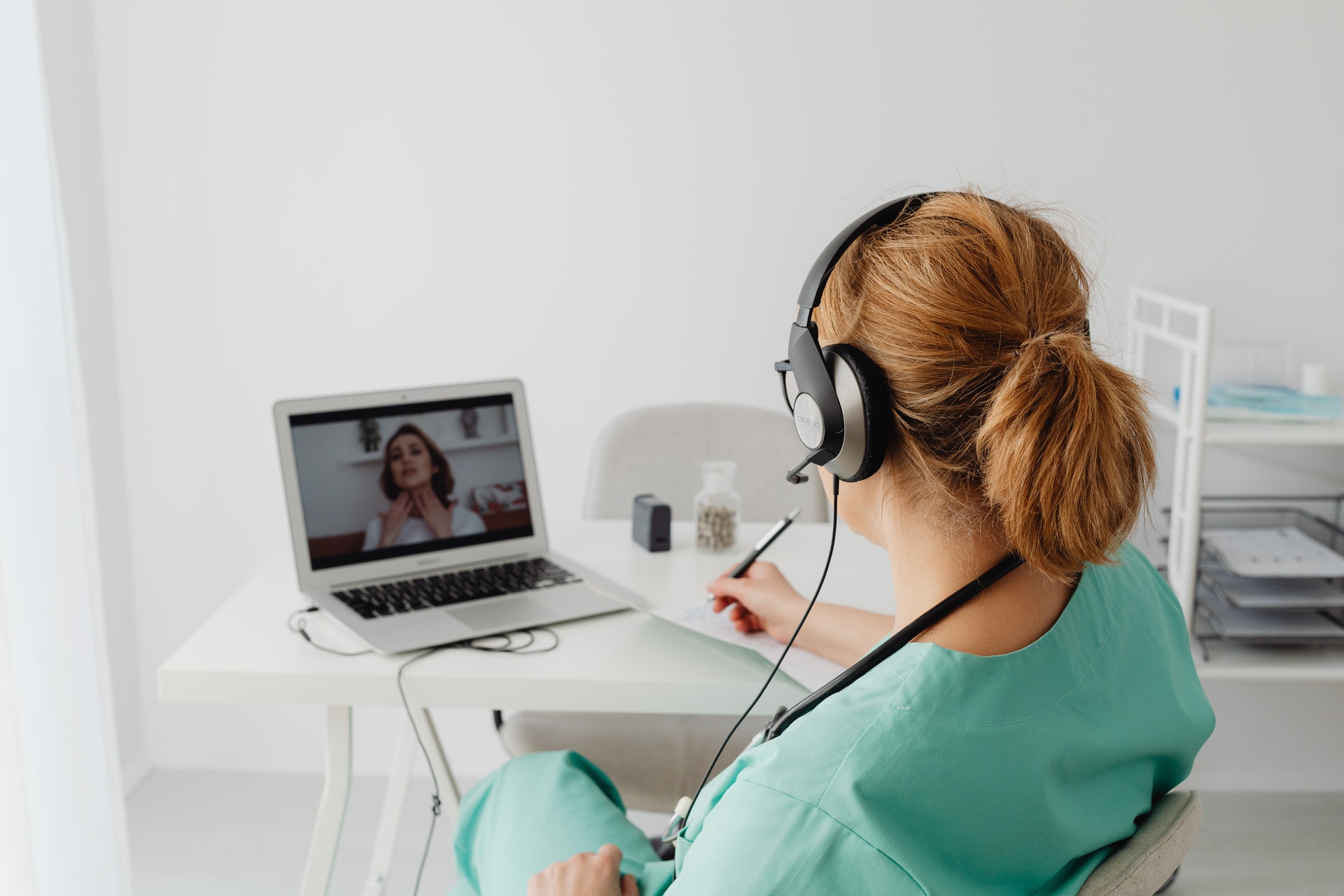
Telehealth and telemedicine
The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) is the network of medical devices and applications, connected by networks, that capture and transmit data. IoMT could help reduce the cost of healthcare and increase patient safety while improving outcomes.
IoMT devices can be used to monitor patients remotely, collect data automatically and then alert clinicians when necessary. They can also be used in the operating room to give physicians access to critical information during surgery.
Future trends in the IoMT industry
In the next 2 years, the Internet of Medical Things (IOMT) is going to go through a period of rapid growth. This includes devices like smart pills, wearable sensors, medical equipment, and more. According to a report by Statista, the IOMT market will reach 30.9 billion units by 2025. We’re not surprised by this prediction: as technology advances, there’s no reason why doctors can’t measure your pulse on your wristwatch or hear your heartbeat through your pacemaker mobile apps.
The research firm Markets and Markets predicts that the IOMT market will grow at an annual rate of 38% in the next 5 years. They believe that North America will be a big driver of this growth. This makes sense: with plenty of venture capital funding and a culture that values innovation, North America is leading the way in terms of developing new IOMT products.
It’s easy to see how this transformation could eventually lead to a society where we have access to our personal health data 24/7, use virtual doctors for minor issues like headaches or stomach pain, and take medicines that are custom-made from our DNA samples
Use of the Internet of Medical Things & Its Benefits
One of the most exciting advancements in the medical field is the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT). This refers to interconnected medical devices and healthcare technology that can share data with doctors, nurses, and other clinical staff.
Diagnostics and treatment procedures, remote monitoring of patients’ vital signs, maintaining patient information, and pharmaceutical management are all conceivable applications for IoMT. The advantages of IoMT are numerous; it will improve patient care, improve clinical outcomes, increase healthcare efficiency, lower costs, and free up time for doctors and nurses to focus on providing quality treatment to their patients. For example:
– IoMT devices allow doctors to monitor patients remotely after they have left the hospital.
– A dose administration aid (DAA) is a device that helps ensure that patients take their medication at the right time and in the right dosage.
– Electronic prescribing systems can be used by doctors to electronically send prescriptions directly to pharmacies without having to rely on paper or faxes.
Patient monitoring equipment that can be accessed remotely
The COVID-19 pandemic has created an emergent need for remote patient care across several countries globally to mitigate the risk of transmission of the disease between patients and healthcare providers.
The IoMT allows doctors to monitor their patients remotely, which can increase their quality of life by reducing the need for in-person visits at hospitals or doctor’s offices. This approach can also help doctors identify problems early on so they can intervene before they become serious issues that would require hospitalization. For instance, if you have diabetes and your blood sugar goes below a certain level, your doctor might be able to send you an alert via text message or email instructing you what steps should be taken next. More data for doctors means more effective diagnoses and treatments. Patients who can monitor themselves remotely are less likely to need frequent hospitalization and may be able to detect problems before they become too severe.
Challenges of implementing the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) is currently revolutionizing healthcare outcomes and transforming the way we approach patient care. From the first time a person becomes a patient, the IoMT can be used to collect data and make recommendations for improved health outcomes. However, there are several challenges associated with implementing IoMT technology that affects healthcare providers and consumers alike.
Healthcare providers must balance new technology with HIPAA compliance, which presents its own set of challenges. The risk of cyberattacks on IoMT devices is high, and medical professionals and hospital administrators must take measures to protect patient privacy. Additionally, hospitals face significant costs of implementation due to the need for new infrastructure, training staff, and integrating patients into the system.
Patients must also adapt to incorporating IoMT devices into their everyday lives to see the full benefits of telehealth. These devices are not always user-friendly, and many patients find them challenging to operate or ineffective in monitoring their conditions. Patients must also be proactive about tracking their health by frequently checking in with their doctors via IoMT devices.
Some of the biggest challenges faced by IoMT providers include IoT platform interoperability, device security, system performance and scalability, integration with other connected devices, efficient patient monitoring, and real-time data analysis.
The internet of medical things will continue to grow, and there is both opportunity and challenges in that growth. The internet of medical things (iomt) is expected to become a huge industry, it is emerging as an important tool for healthcare providers.



2 thoughts on “The internet of medical things: trends and concerns (IoMT)”